Wow! Isn’t it amazing how fast that year seems to have passed? So many big events and important factors having an influence on financial markets (Brexit, US presidential election, monetary policy by central banks etc.).
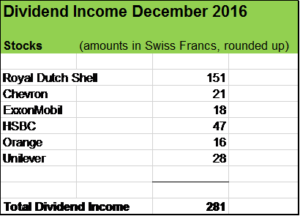
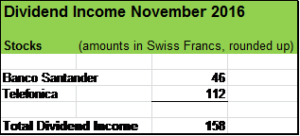
My portfolio has done pretty well so far and my dividend income for December 2016 (net dividend payments received in Swiss Francs which trades more less at parity to the USD) increased year to date by around 2o % due to the acquisition of HSBC stocks, organic dividend increases and dividend reinvestments.
Royal Dutch Shell (RDS)
In 2009, I acquired 200 stocks of RDS for around CHF 5’000 and since then consistently reinvested all dividends into the same company. Today, the stock count stands at 290, an increase of almost 50 % in seven years. That’s the magic of the compound effect! Also considering the stock price increase since 2009 that investment has paid off handsomely so far.
Today, RDS is to some extent a different business mainly due to the acquisition of the British multinational oil and gas corporation BG Group. After the combination, RDS is one of the world’s top liquified natural gas company. Over the medium and longer term that acquisition may substantially strengthen RDS and has already positioned the company as the world’s second-largest public oil and gas company behind ExxonMobil. But that move also led to an elevated leverage. In combination with a low oil price level which puts pressure on the generation of free cash flow this is to the substantial detriment of the risk position and the financial flexibility of the company.
It seems, that the acquisition is quite well on track. The company is committed to reduce debts mainly through asset sales and “pledged” to keep its “iconic dividend” intact. The last time, RDS had to cut its dividends was 1945 and since then, decade over decade, shareholder benefitted from increasing payments.
Chevron Corporation (CVX)
Plummetting oil and gas prices forced CVX to streamline, which the company did at an amazing pace. CVX is also vigorously slashing capital spendings. The company targets a positive Free Cash Flow after dividends by 2017. With mega-projects coming online in the next quarters they substantially contribute to the company’s cash flow and profit generation. With these projects ramping up, less capital spending is needed, revenues and operational cash flow are expected to improve significantly even in a low oil price environment. For the future, CVX is set to focus on less capital intense, shortcycle and high margins projects and underlined its priorities in deleveraging and increasing dividends over time.
CVX increased its quarterly dividend for the fourth quarter from USD 1.07 to USD 1.08 per share, that’s the 29th consecutive year the company elevated its dividend payout. The last hike is relatively small but an important message to us shareholders underlining the confidence in the company’s financial strength and optimism regarding future performance.
Exxon Mobil Corporation (XOM)
Compared to the other oil-majors, XOM is very strong from a financial standpoint and robust in terms of operational results. But plummetting oil and gas prices took a toll on that company too, putting free cash flow and profits under enormous pressure. The debt level more than doubled in recent years. In April 2016, the rating agency Standard & Poors downgraded XOMs Rating from AAA to AA+ Outlook stable. The downgrade is in my view more symbolic than effectively to the detriment of the borrowing conditions of XOM. AA+ is still very comfortable.
XOM has paid dividends for more than 100 years! In April 2016, the company increased the dividend by 2.7 %. This makes 34 years of consecutive annual dividend hikes in a row!
As an integrated oil company with such strong upstream and downstream operations and with one of the largest chemical businesses of the world, XOM should be able to adapt to a prolonged period of low oil and gas prices and deliver robust results in the future.
Hongkong and Shanghai Banking Corporation (HSBC)
HSBC is one of the largest banking and financial services companies in the world, headquartered in London.
I acquired the stocks ahead of the Brexit vote, when I felt that they traded at a significant discount to book value per share and price earings ratio looked attractive. The company is diversified and well positioned in growth markets, mainly in asia. The debt profile seems relatively robust.
There is no questions there a several challenges for the company. As a global bank in an ultra low interest rate environment with falling revenues and high regulatory requirements HSBC is certainly facing strong headwinds. As a systemically relevant bank HSBC has to fulfill capital requirements expressed in the Tier 1 Common Capital Ratio (CET) which puts the bank’s core equity capital in relation to its total risk-weighted assets and signifies the financial strength. HSBC made significant progress in this respect being able to boost the CET from below 12 % to 13.9 % (compared to the previous year). This was mainly achieved by the disposal of assets in Latin America.
The third quarter earning report shows that the company also made progress regarding operating expenses and achieved a positive jaws in 3 Q 2016 which means that HSBC – being confronted with falling revenues – managed to slash spendings even faster and to protect the profitability (see blogpost Positive Jaws Ratio improves finances).
The company announced to hold the dividend steady and started a share buy-back program this summer expected to finish early 2017.
Orange SA (ORA)
Orange is a French multinational telecommunication Company with over 250 millions customers around the world and over 170’000 employees.
After some years of declining profits due to weaknesses in its main market France and due to cut throat competion in the European telecommunication market, Orange’s last quarterly earning reports showed steadily improving results. Being in my view a fine business, it seems to me that I overpaid, when I acquired stocks of Orange in 2010. Even taking into account the dividends collected in the past six years, the total return of that investment is more or less zero.
But I still like my position in Orange, the fundamentals and growth catalysts look just fine to me. The company is so large and well positioned in attractive markets and benefits from a strong name. What I also like is the sound financial condition with a moderate debt level.
Unilever (ULVR)
I like that company for its attractive and stable business model, the strong brands with household names and products such as Lipton Ice Tea, Magnum Ice Cream, Axe, Rexona, Knorr, Persil etc. The company is broadly diversified, well positioned and should benefit from several catalysts for future growth and being able to comfortably weather headwinds in some markets.
The current dividend yield at costs of my investment stands at 3.6 %. In the past decades, earnings per share and dividend grew decently around 5 % per year which makes the business a stable cash generation machine.
How was your December in terms of dividend income?
Disclaimer
You are responsible for your own investment and financial decisions. This article is not, and should not be regarded as investment advice or as a recommendation regarding any particular security or course of action.